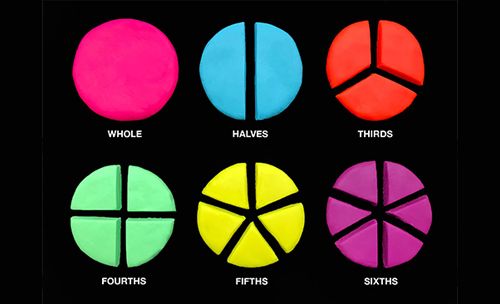
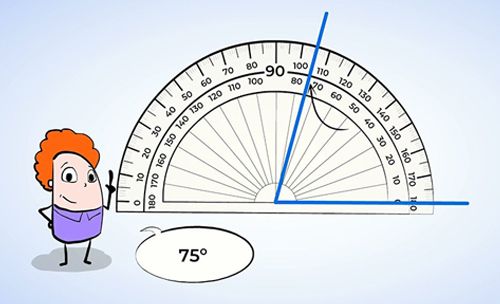
The “ Fifth and Sixth Grade” exhibition contains a set of exhibits and activities to illustrate mathematical concepts and basics in a fun and interesting technical style that stimulates the scientific curiosity of the students and their teachers
The objectives of the exhibition are centered on the following:
- Transforming mathematics from a science described as rigid to an educational pleasure.
- Integrating the two stages of education directly into the experimental process in mathematics by letting the students conduct experiments themselves or interact directly with the exhibits and observe the results.
- Developing school teachers’ understanding of mathematics for fifth and sixth grades as a dynamic experimental concept based on knowledge and inquiry.
- Improving the ability of school teachers to make appropriate educational decisions by taking into account the needs related to the variety of curricular topics at these stages.
- Increase the effectiveness of math teaching methods and the necessary methods in the teaching process.